Product vs Period Costs Accounting for Managers
By accurately identifying and categorizing these costs, businesses can create more precise budgets that reflect actual expenses. Effective budgeting helps organizations allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that funds are available for essential activities, such as marketing and research and development. Additionally, managing period costs enables organizations to identify areas for potential savings, ultimately contributing to improved profitability. Period costs can be further classified into different categories based on their nature and purpose. Some common of period costs include selling and marketing expenses, administrative expenses, and research and development costs.
Is Converting Your Personal Vehicle for Business Use a Good Idea?
These expenses are deducted from revenues to calculate operating income, reflecting the costs incurred to support the business’s ongoing operations. Factory rent, for instance, is Bookkeeping for Chiropractors a period cost that benefits multiple production lines or departments. Utilities, such as electricity, water, and heating, are also indirect costs that are used by various departments within the organization. The preceding list of period costs should make it clear that most of the administrative costs of a business can be considered period costs.

Optimizing Accounting Reserve Account Management Strategies
Other companies include fringe benefit costs in overhead if they can be traced to the product only with great difficulty and effort. Direct allocation provides a simple and transparent way to assign costs to cost objects, making it easier to trace expenses and calculate the true cost of producing goods or services. However, not all Period Costs can be directly allocated, especially those that benefit multiple cost objects simultaneously.

Limitations and Challenges of Period Cost Analysis
- The opening WIP is the cost of unfinished services from the previous period, while the closing WIP is the cost of services not completed at the period’s end.
- Period costs can be separated by category on the income statement to help understand what the costs are and how much is spent on each.
- The period costs could not be capitalized since they are not directly tied to the manufacture of inventory and are thus charged in the company’s profit and loss statement.
- These expenses are not directly tied to inventory production and so do not constitute part of the cost of goods sold and are charged in the company’s income statement.
- Choosing the appropriate method of allocating Period Costs depends on factors such as the nature of the business, the complexity of operations, and the availability of data.
- Fixed costs remain constant for a given tenure, irrespective of the level of output.
Only when the product is sold do these costs get recognized as an expense, which is matched against the sales revenue to help determine the profit for the period. The period cost is important and a necessary thing period costs include to keep track of because it allows you to know your company’s net income for each accounting period. Keeping track of the period of cost is also important for filing accurate business taxes and for preparing for an audit. Tracking period costs will also help a business balance its budget and gain savings.
- Out of the total costs, 70% were attributed to the cost of goods sold, 10% to work in progress, and 20% to finished goods inventory.
- Understanding Period Costs is crucial for any business looking to navigate the complex landscape of financial management.
- Period costs, however, are expensed entirely in the current period since they relate directly to this timeframe.
- Marketing expenses can be categorized into several types, including digital marketing, print advertising, public relations, branding and design, and market research.
- It is essential for companies to accurately categorize and document these expenses to ensure they are maximizing their tax deductions.
- Calculated in advance, they play an important role in budget preparation, considering all factors affecting such costs.
Recognizing the importance of Period Costs in financial analysis allows businesses to make informed decisions, optimize performance, and achieve long-term success and sustainability. Indirect Allocation involves distributing Period Costs to cost objects based on predetermined allocation bases. These allocation bases may include factors such as labor hours, machine hours, square footage, or production volume. Unlike capital expenditures, which can provide long-term benefits, period costs are usually related to the day-to-day operations of a business. To quickly identify if a cost is a period cost or product cost, ask the question, “Is the cost directly or indirectly related to the production of products? The cost of rent can vary depending on factors such as location, size of the office space, and local real estate market conditions.
- If the company temporarily shuts down activities or facilities, standby costs will remain.
- Additionally, the allocation of costs is different for product costs and period costs.
- Period costs may include both fixed and variable elements, such as rent (fixed) and sales commissions (variable).
- Administrative expenses are non-manufacturing costs that include the costs of top administrative functions and various staff departments such as accounting, data processing, and personnel.
- Routine maintenance costs may be fixed, while repair expenses vary depending on the frequency and extent of equipment breakdowns.
- All manufacturing expenses, costs incurred in the factory or production process, (i.e., direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead) are product costs.
Marketing Expenses
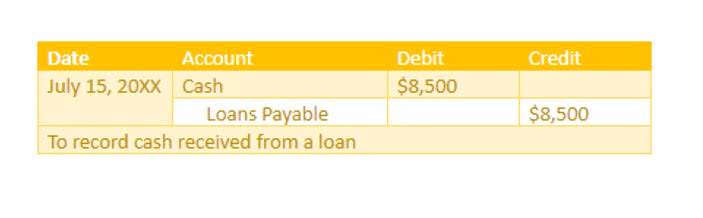
In addition to indirect materials and indirect labor, manufacturing overhead includes depreciation and maintenance on fixed assets machines and factory utility costs. The $10 direct materials would be a debit to cost of goods sold (increasing) and a credit to inventory (decreasing). Resource Allocation is a crucial aspect of cost accounting that allows businesses to assign expenses to specific cost objects, such as products, services, or departments. This helps organizations make informed decisions and manage their resources effectively. Period costs are expenses related to business operations during an accounting period, recorded as operating expenses on the income statement. For instance, let’s consider a scenario where a company is considering expanding its product line.
